Validity (accuracy): The extent to which a test measures what it is supposed to measure.
Sensitivity:
1. Ability of test to correctly classify an individual as diseased.
2. The probability of being tested positive when the disease is present.
| D(+) | D(-) | |
| T(+) | A TP | B FP |
| T(-) | C FN | D TN |

SnNOUT: Highly sensitive test, if negative, rules out the disease
Specificity:
1. Ability of test to correctly classify an individual as disease-free.
2. Probability of being test negative when disease is absent.

SpPIN: Highly specific test if positive rules in the disease.
Predictive Value:
Positive predictive value (PPV):
1. % of patients with positive tests who actually have the disease
2. Probability of patient having the disease when the test is positive

Negative predictive value (NPV):
1. % of patients having disease when test is positive
2. Probability of patient having the disease when the test is positive

Bayes Theorem:

PPV: Highly dependent on prevalence of disease
Factors affecting PPV (in decreasing order):
- Prevalence
- Specificity
- Sensitivity
Parallel testing:
A-test or B-test: (A, B) sensitivity or specificity
Combined sensitivity: Sn= A+B-AB
Combined specificity: Sp=A*B
Sensitivity will increase and specificity will decrease
Series testing:
A-test or B-test: (A, B) sensitivity or specificity
Combined sensitivity: Sn= A*B
Combined specificity: Sp=A+B-AB
Sensitivity will decrease, and specificity will increase
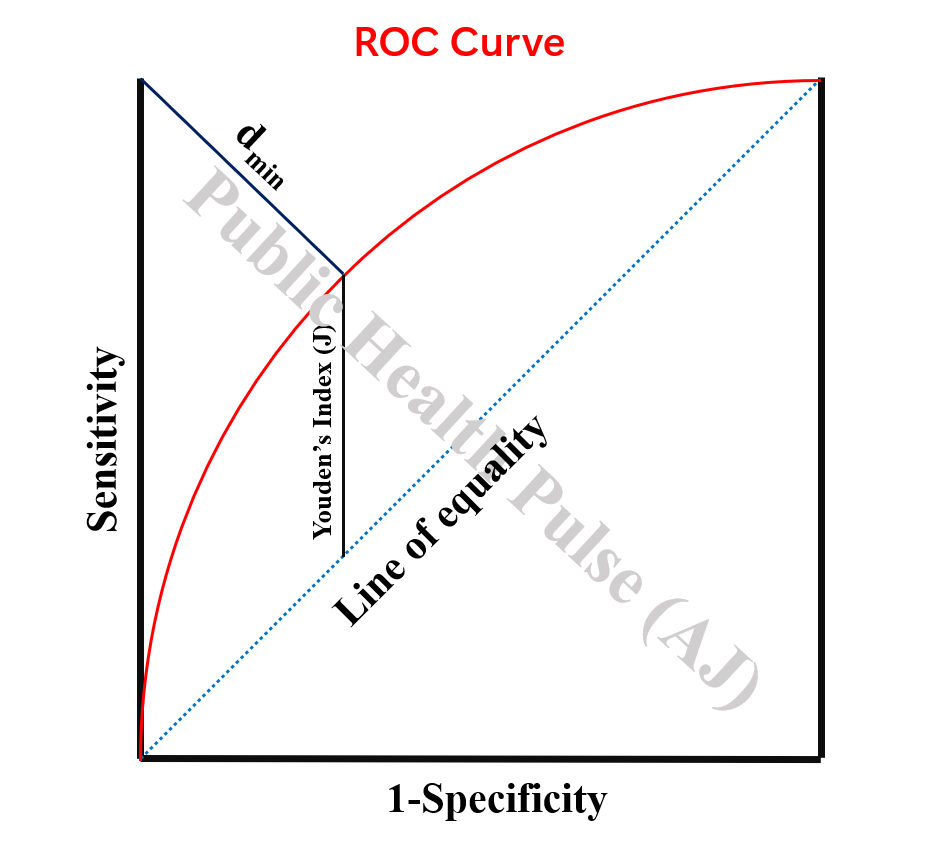
Youden’s index:
It is the maximum vertical distance from the line of equality to the point on the ROC curve
A measure of summary of the ROC curve
It cuts the ROC curve at the point (optimal cut-off point) that optimizes the differentiating ability when equal weight is given to sensitivity and specificity
Likelihood Ratio:
•Likelihood ratio (+): How much the increase in the probability of having the disease if the test result is positive
LR(+) = Sn/(1-Sp)
Likelihood ratio (-): How much decrease in the probability of having the disease if the test result is negative
LR(-) = (1-Sn)/Sp
Diagnostic odds ratio:
It relates the odds that the test is positive in a diseased population to the odds that the test is positive in a healthy population
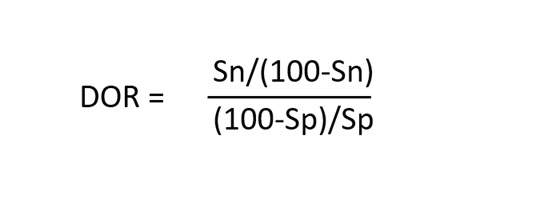
>=50 : Very strong validity of test
20 to <50 : Strong
10 to <20 : Fair
<10 : Weak
Very good https://lc.cx/xjXBQT
Good https://rb.gy/4gq2o4